Lesson 1.9 Calculations
Calculations refer to different calculations to apply between devices. A calculation creates a virtual node that holds the result of the calculation. The data used by the device does not go back in time; instead, it uses data from after the calculation was created. In the device details of the calculated device, you can see which devices are included, what value was used, and the type of calculation. It is one of the most powerful features of the platform and can be used to realize a wide variety of use cases.
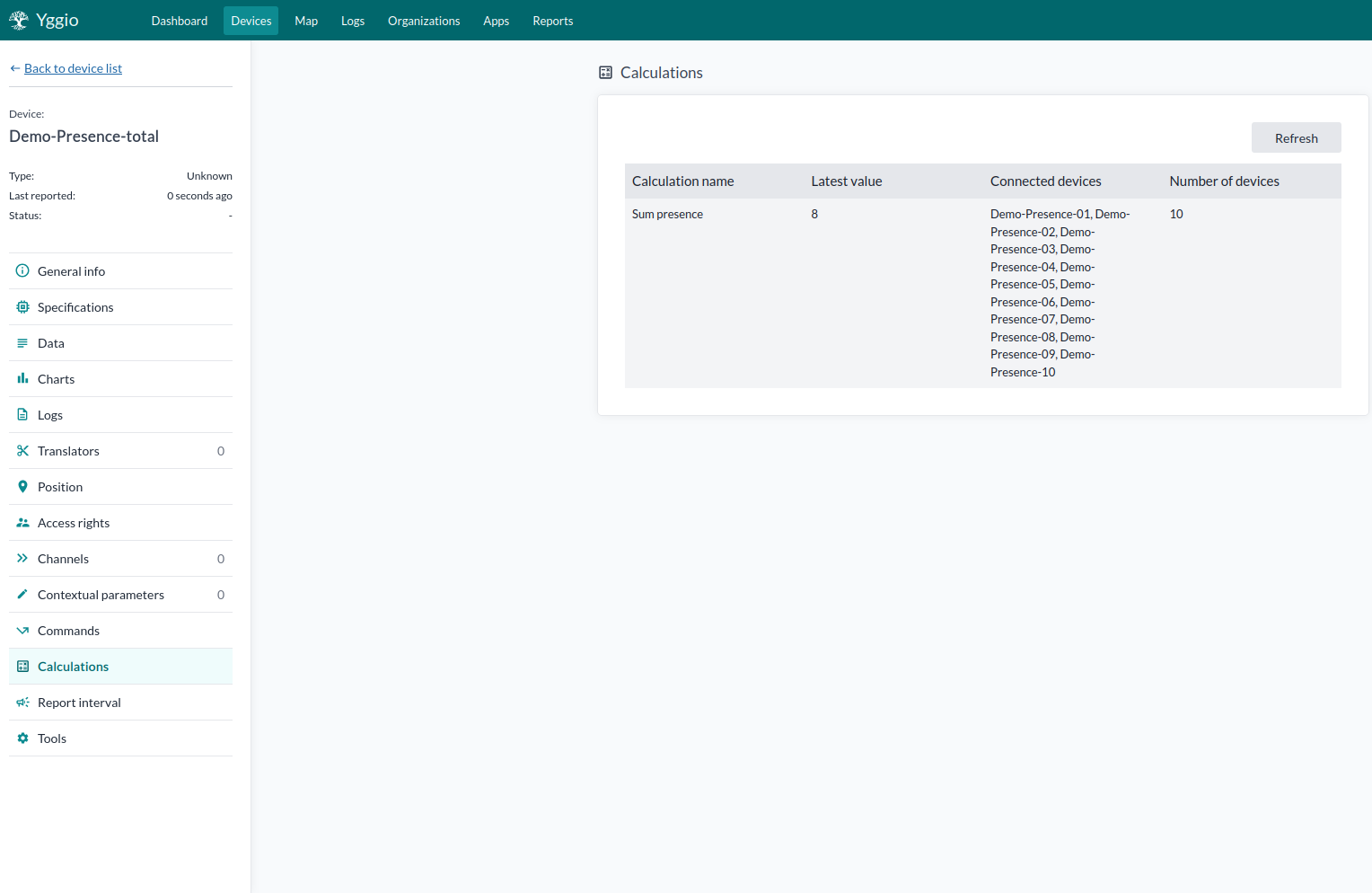
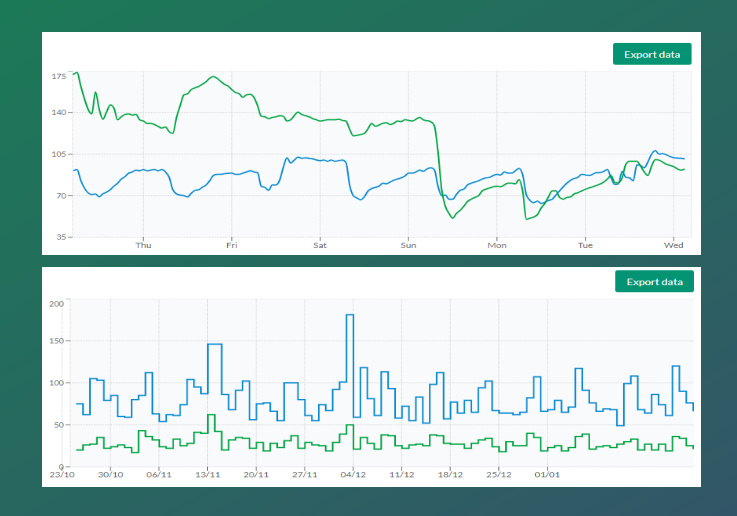
In this lesson, we will explore the available calculation types and learn how each one affects data processing and visualization.
Available Calculations
- Mean: The average value of the last reported values from all devices included in the calculation.
- Minimum: The minimum value of the last reported values from all devices included in the calculation.
- Maximum: The maximum value of the last reported values from all devices included in the calculation.
- First: The first value of the last reported values from all devices included in the calculation.
- Last: The last value of the last reported values from all devices included in the calculation.
- Count: The total number of data points aggregated from the included devices.
- Sum: The sum of all last values from all devices included in the calculation.
- Difference: The difference between the last value from the first device and the sum of values from all other devices included in the calculation. This is typically used to determine the difference between incoming values.
- Derivative: Rate of change between all devices included in the calculation. It is typically used to detect anomalies between different devices when similar change rate was expected.
Create calculated nodes
A calculated node is a device that take a specific value, do a calculation with the data and then display the data as a device. Let's try it out.
- Press "Select Many".
- Select devices to add to the calculation.
- Press "Select Action" and then "Calculate".
- Select the calculation type
- Pick a "Measurement" for your devices.
- Select a name for your calculated device.
- Press "Create".
- Repeat this process for different types of IoT nodes and measurements, and add alarm translators to the calculated node. This allows you to monitor conditions such as whether the average temperature in a building is too high or too low.
- Add calculated nodes to your views and dashboards to enable clear and insightful visualizations.
- Using the Swagger API, you can also direct multiple calculations to the same IoT node.
⚠️ Important:
For cases involving conditional logic, filtering, or custom thresholds, use a data flow or translator instead of calculated nodes.If you need to perform calculations across a large number of devices, a translator is also the preferred option.
The translator feature "Additional Device Update" offers superior scalability compared to calculated nodes, as it operates on incoming events only rather than on stored time series data.
Example Use Cases for Calculated Nodes
Temperature & Environment
- Average temperature across a room, building, or multiple buildings (
mean) - Maximum or minimum temperature in any monitored area (
max,min) - Average indoor air quality score across floors or offices (
mean) - Average humidity in a warehouse zone or production floor (
mean)
Energy & Utilities
- Total energy consumption for a room, floor, building, or campus (
sum) - Water consumption per city, per area, per floor, zone, or building (
sum) - Water loss detected between two sensors in a pipeline (
difference) - Change rate of water volume in wells during rainfall or post-drainage (
mean) - Total volume across multiple tanks or silos (
sum) - Average tank fill level across storage units (
mean)
Occupancy & Usage
- Seat occupancy count per area or building (
sum) - Seat utilization ratio (
meanoccupancy / total capacity) - Meeting room utilization percentage across a zone (
mean) - Total usage time of shared assets or spaces (
sum) - Device message count (e.g., total number of updates received) (
count)
Specialized Use Cases for Calculated Nodes
Some of these more advanced use cases may require an additional translator to preprocess or transform the raw data—such as inverting values or applying custom logic—before it can be used in a calculated node. When used in Reports, the final adjustments to a KPI can also be handled with an Excel formula, allowing for greater flexibility and presentation control.
HVAC and Indoor Climate
- Temperature gradient between rooms or floors (
difference) - Differential pressure between two points in a ventilation system (
difference) - Average CO₂ level during occupancy hours only (
mean, time-filtered) - CO₂ trend speed over a defined period (
rate of change) - Max temperature drift per hour (e.g., sudden HVAC failures) (
rate of change) - Average daily cooling/heating demand derived from setpoint vs actual temp (
mean of difference) - Minimum air flow rate in ventilation system per zone (
min)
Energy Optimization & Fault Detection
- Peak power usage during working hours (
max, time-windowed) - Night-time power leakage in unused zones (
sum, with condition) - Abnormal energy consumption detection (baseline vs actual,
difference) - Power factor analysis across industrial devices (
derived metric) - Solar production vs consumption delta per hour (
difference)
Industrial & Manufacturing
- Cycle time average across machines or production lines (
mean) - Downtime calculation based on status flag or activity absence (
countgaps) - Max pressure drop across filters (use
maxdifference from reference) - Maximum load recorded on industrial machinery (
max) - Cooling fluid loss over time (
difference, with starting value) - Average vibration amplitude per hour or shift (
mean)
Water Management & Environmental Monitoring
- Evaporation rate from open reservoirs (
rate of change) - Average rainfall vs inflow correlation across pump stations (
mean, across sensors) - Total overflow events in combined sewer systems (
count) - Water level delta before/after storm event (
difference) - pH value drift over 24 hours (
rate of change, smoothed)
Space Utilization & Smart Building
- Real-time capacity ratio of a co-working area (
current occupancy / capacity) - Time-weighted average occupancy per day (
mean, weighted) - Utilization heatmap input by aggregating movement sensor data (
sum) - Percentage of unused desks over time (
inverse meanoccupancy) - Meeting room idle time ratio (
differencebetween reserved and used)
Logistics & Smart City
- Average package flow through a zone (
count, normalized by time) - Number of garbage pickups missed (
expected - actual) - Traffic congestion index using travel time deltas (
difference) - Noise pollution average during nighttime (
mean, night hours only) - Vehicle charging station utilization rate (
active sessions / total ports)